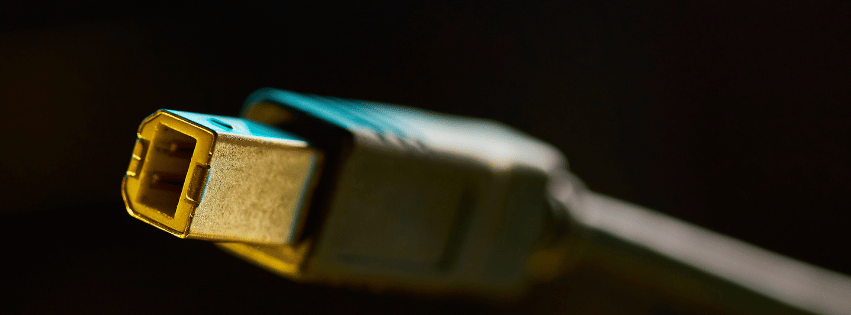In today’s gadget-driven world, USB cables have become an indispensable part of our daily lives. From charging smartphones to connecting devices, these cables vary widely in shape, size, and function. This guide will illuminate the visual differences and uses of the most common USB cable types, ensuring you select the right cable with ease whether you’re just trying to purchase the right one for your personal needs, or if you’re in need of bulk USB cable assembly manufacturing for industrial or business applications. If the latter applies to you and you need a reliable cable manufacturing partner, please contact us at [email protected] with your cable drawing and required specifications!
Most Common USB Cable Types Explained
1. USB-A
Visual Identification: The quintessential USB connector, USB-A is a flat and rectangular plug that’s often found at one end of most USB cables. It usually connects to host devices such as computers or power outlets.
Introduction and Use: Introduced in the mid-1990s, USB-A remains the standard for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and external storage devices. Commonly used for data transfer as well as charging, it supports data transfer rates of up to 480 Mbps for USB 2.0 versions and up to 5 Gbps for USB 3.0.

2. USB-B
Visual Identification: USB-B connectors are noticeably square with beveled corners on the top. They are less common in consumer electronics and are often seen connecting to larger devices like printers and scanners.
Introduction and Use: Around since the original USB standard, USB-B is primarily used for data transfer and charging larger devices. With USB 3.0 variations, identifiable by additional pins and often a blue internal color, data transfer speeds can reach up to 5 Gbps.
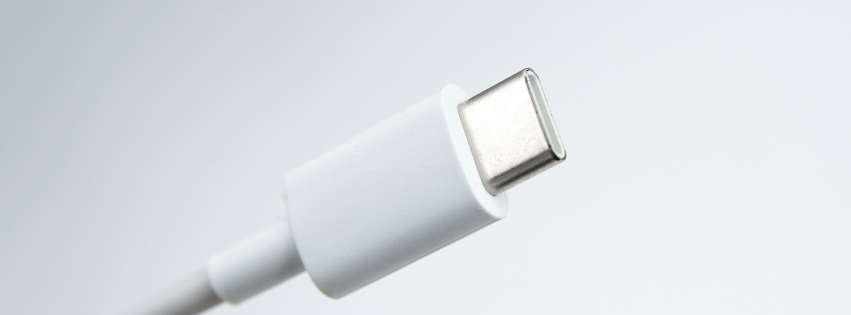
3. USB-C
Visual Identification: Featuring a small, sleek, and oval design, USB-C is reversible, meaning it can be plugged in either way without issue—an ergonomic advantage.
Introduction and Use: Introduced in 2014, USB-C has quickly become the universal standard in modern devices, prevalent in smartphones, laptops, and tablets for both data transfer and charging. It supports up to 10 Gbps for USB 3.1, speeds of 20 Gbps for USB 3.2, and is capable of 40 Gbps with Thunderbolt 3 and 4 technology.
4. Mini-USB
Visual Identification: Mini-USB comes in a smaller size than USB-A or USB-B, with a trapezoidal shape. It’s typically found in old models of MP3 players and cameras.
Introduction and Use: Common in the early-to-mid 2000s, mini-USB served for connecting smaller personal electronics and offered 480 Mbps data transfer rates like USB 2.0.
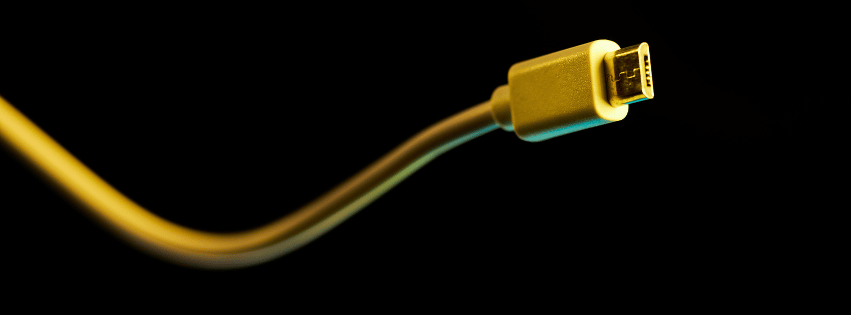
5. Micro-USB
Visual Identification: A more compact connector than mini-USB, micro-USB has a flatter and narrower form, and is somewhat trapezoidal with a wider top.
Introduction and Use: Released in the late 2000s, micro-USB became the standard for older Android phones and various portable devices, offering data speeds up to 480 Mbps (USB 2.0) and charging capacities.
Exploring Lesser-Known USB Variations
While the more common USB types tend to dominate the scene, it’s important to also recognize some of the less common variants. These connectors cater to specific devices and uses, and understanding them can offer a complete picture of the USB landscape.
1. USB-A SS (SuperSpeed USB-A)
Visual Identification: A step up from the traditional USB-A, the USB-A SS connector can often be identified by a blue color inside the port (though this isn’t always the case). The external shape remains the same as the standard USB-A.
Introduction and Use: As part of the USB 3.0 standard introduced in 2008, USB-A SS supports faster data transfer speeds of up to 5 Gbps. This variant is used extensively in devices that require rapid data transmission, such as external hard drives and Solid-State Drives (SSDs), allowing for efficient data backups and file transfers.
2. USB Mini-B
Visual Identification: The USB Mini-B connector resembles the mini-USB type with its slightly trapezoidal shape, yet it contains an additional pin compared to the standard mini-USB.
Introduction and Use: Often found in older camera models and some legacy mobile devices, this connector type was popular in the early 2000s. While being largely phased out in favor of micro-USB or USB-C, mini-B was pivotal for synchronizing and charging smaller electronics at data rates up to 480 Mbps.
3. USB 4-Pin
Visual Identification: The USB 4-pin looks like a simplified version of the larger USB connectors, often used in uncommon situations to deliver specific functions. It lacks the notch and traditional USB housing seen in other types.
Introduction and Use: It’s typically seen in proprietary systems or specialized applications, providing both power and data transfer but at limited rates compared to mainstream USB styles. Primarily, its function depends on the device it was designed for, making it less adaptable.
4. Micro-B and Micro-B SS (SuperSpeed Micro-B)
Visual Identification: The Micro-B connector is quite similar to micro-USB but has a slightly different pin setup, with additional connections visible. The SuperSpeed Micro-B variant is known for its bifurcated form: one standard micro-USB side and an additional smaller pin section.
Introduction and Use: Micro-B was primarily used in smartphones and tablets before USB-C standardization. With the advent of formats like USB 3.0, the Micro-B SS version found its place in external hard drives, enabling SuperSpeed data transfers up to 5 Gbps, thereby enhancing external storage performance considerably, before being mostly replaced by the more ergonomic and faster USB-C.
Specifications and Usability
Knowing your USB cables doesn’t just help in identifying them visually, but also helps understand their specifications regarding data transfer and usage contexts. USB 2.0, 3.0, and beyond vary in their data transfer capabilities, where higher versions offer backward compatibility but greatly increase transfer rates. Understanding these distinctions can help in choosing the right cable for either transferring files or efficiently charging a device.
Conclusion
Understanding USB cable types can simplify connecting your devices, maximizing performance, and ensuring compatibility. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or simply dealing with the cords that power your world, knowing which cable goes where is invaluable.
At Technical Cable Applications, we specialize in the bulk manufacturing of a wide range of cable assemblies, from USBs to other essential data and power solutions like Ethernet, M12, and coaxial cables. We hope this guide serves your needs and helps you navigate the vast landscape of USB technology with confidence. If you’re in need of USB cable assembly manufacturing for your business, government or industrial needs, please contact us at [email protected] with your cable drawing and any necessary NDAs!